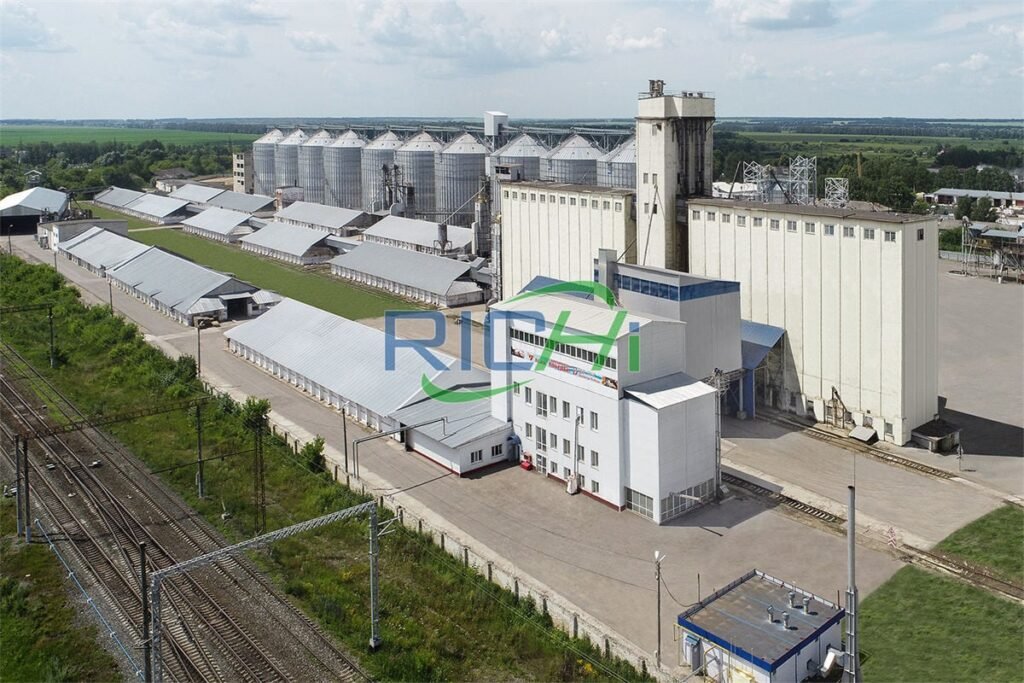
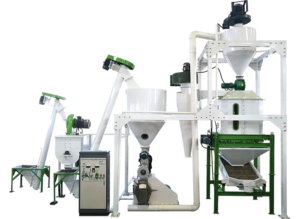
In the rapidly expanding pet care industry, the demand for high-quality pet food is surging. With the rise in pet ownership and increased awareness of pets’ nutritional needs in Russia, establishing a state-of-the-art pet food production facility presents a lucrative opportunity.
Designing a 6 T/H (tons per hour) pet food production line in Russia requires meticulous planning, specialized knowledge, and compliance with local and international standards. This guide outlines the essential steps and considerations for creating a cutting-edge pet food manufacturing facility tailored to the Russian market.
Step 1: Market Research and Feasibility Study
Conduct thorough market research and a feasibility study to understand the Russian pet food market, identify potential challenges, and formulate a robust business plan.
Key considerations:
- Market Demand: Analyze the demand for various pet food types, considering pet ownership trends, consumer preferences, and market segments.
- Competitive Landscape: Assess existing pet food manufacturers and identify competitive advantages for your production line.
- Regulatory Environment: Understand Russian regulations on pet food production, labeling, and distribution.
- Raw Material Availability: Evaluate the availability and cost of essential raw materials like proteins, grains, vitamins, and minerals.
- Economic Factors: Consider economic variables such as currency fluctuations, import/export regulations, and potential government incentives.
Step 2: Facility Location and Layout Design
Choose a strategic location for your facility, considering:
- Proximity to Raw Materials: Minimize transportation costs and ensure ingredient freshness.
- Transportation Infrastructure: Ensure good road and rail connections for efficient product distribution.
- Utilities: Verify reliable access to essential utilities like electricity, water, and natural gas.
- Labor Pool: Select an area with a skilled workforce familiar with food production processes.
Collaborate with architects and engineers to design an efficient facility layout, focusing on:
- Production Flow: Optimize material flow from raw storage to processing, packaging, and shipping.
- Hygiene Zones: Clearly separate different hygiene zones to prevent cross-contamination.
- Future Expansion: Design for potential future growth.
- Energy Efficiency: Incorporate energy-efficient design elements.
Related post: https://www.pellet-richi.com/pellet-production-line
Step 3: Equipment Selection and Process Design
Select equipment that ensures the desired 6 T/H production capacity while maintaining product quality. Key components include:
- Raw Material Handling and Storage: Efficient silos, bins, and conveying systems.
- Grinding Equipment: Hammer mills or roller mills for size reduction.
- Mixing Systems: Ribbon blenders or paddle mixers.
- Extrusion System: Single or twin-screw extruders.
- Drying Equipment: Multi-pass dryers.
- Coating Systems: For applying fats and flavors.
- Cooling Equipment: To bring products to ambient temperature before packaging.
- Packaging Line: Automated systems for weighing, filling, and sealing packages.
Design the process flow to ensure:
- Recipe Flexibility: Handle various pet food formulations.
- Quality Control Points: Integrate in-line quality control measures.
- Cleaning and Sanitation: Facilitate easy cleaning and sanitization.
- Automation: Enhance efficiency and consistency with automation systems.
Step 4: Quality Control and Food Safety Systems
Implement robust quality control and food safety systems, including:
- HACCP Plan: Develop a specific Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points plan.
- Quality Control Laboratory: Establish an on-site lab for testing.
- Traceability System: Track ingredients and products through the supply chain.
- Allergen Management: Prevent cross-contamination with strict protocols.
- Pest Control: Implement integrated pest management.
- Employee Training: Train staff on food safety, hygiene, and quality control.
Step 5: Regulatory Compliance and Certification
Ensure compliance with relevant regulations:
- Russian Pet Food Regulations: Adhere to local laws on production, labeling, and distribution.
- International Standards: Consider certifications like ISO 22000 or FSSC 22000.
- Export Compliance: Meet regulations in target export markets.
- Labeling Requirements: Design compliant packaging and labels.
Step 6: Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Incorporate sustainability into your design:
- Energy Efficiency: Use energy-efficient equipment and processes.
- Water Management: Implement water recycling and treatment systems.
- Waste Reduction: Minimize waste and explore recycling opportunities.
- Sustainable Packaging: Use eco-friendly packaging options.
Step 7: Workforce Planning and Training
Develop a skilled workforce:
- Staffing Plan: Identify key roles and required skills.
- Recruitment Strategy: Target individuals with relevant experience.
- Training Programs: Provide thorough training on all production aspects.
- Continuous Education: Offer ongoing training and development.
Step 8: Supply Chain and Logistics Planning
Ensure efficient supply chain management:
- Supplier Relationships: Build strong relationships with reliable suppliers.
- Inventory Management: Implement efficient systems to manage stock levels.
- Distribution Network: Develop a robust network for product delivery.
- Cold Chain Management: Ensure proper cold chain management for wet pet food.
Designing a 6 T/H pet food production line in Russia is a complex yet rewarding endeavor. By following these steps and considering the unique aspects of the Russian market, you can establish a state-of-the-art facility capable of producing high-quality pet food that meets the needs of Russian pet owners and their pets.
Success in the pet food industry relies on efficient production and developing products that meet the nutritional needs and preferences of pets and their owners. Stay attuned to market trends, invest in R&D, and commit to quality and safety to ensure the long-term success of your pet feed production line in Russia.